At a time when sustainability and energy efficiency are key, it is important to make the best use of all available resources. A rapidly emerging source in the world of renewable energy is waste heat. But what exactly is waste heat and how can we harness it to make our society greener and more efficient?
In this blog, we will take you through the fascinating world of waste heat. We will explore the basics, name the benefits of using waste heat and show how waste heat can play a crucial role in the pursuit of a more sustainable future.
Do you want your innovation to make it easier to meet ESG targets? Would you like to develop your idea in collaboration with Beeliners? We would love to help you! Feel free to drop by for a cup of coffee and we will be happy to discuss the possibilities with you.
What is waste heat?
Amid growing pressure to make our energy supply more sustainable, we are increasingly casting a glance at alternative sources such as solar and wind energy. However, there is an equally powerful and misunderstood source that can contribute significantly to our sustainability goals: waste heat. But what exactly lies behind this term?
Residual heat is nothing less than the heat released as a by-product of various industrial processes and plants. It is, as it were, the leftover heat generated during production processes, heat that often remains unused until now.
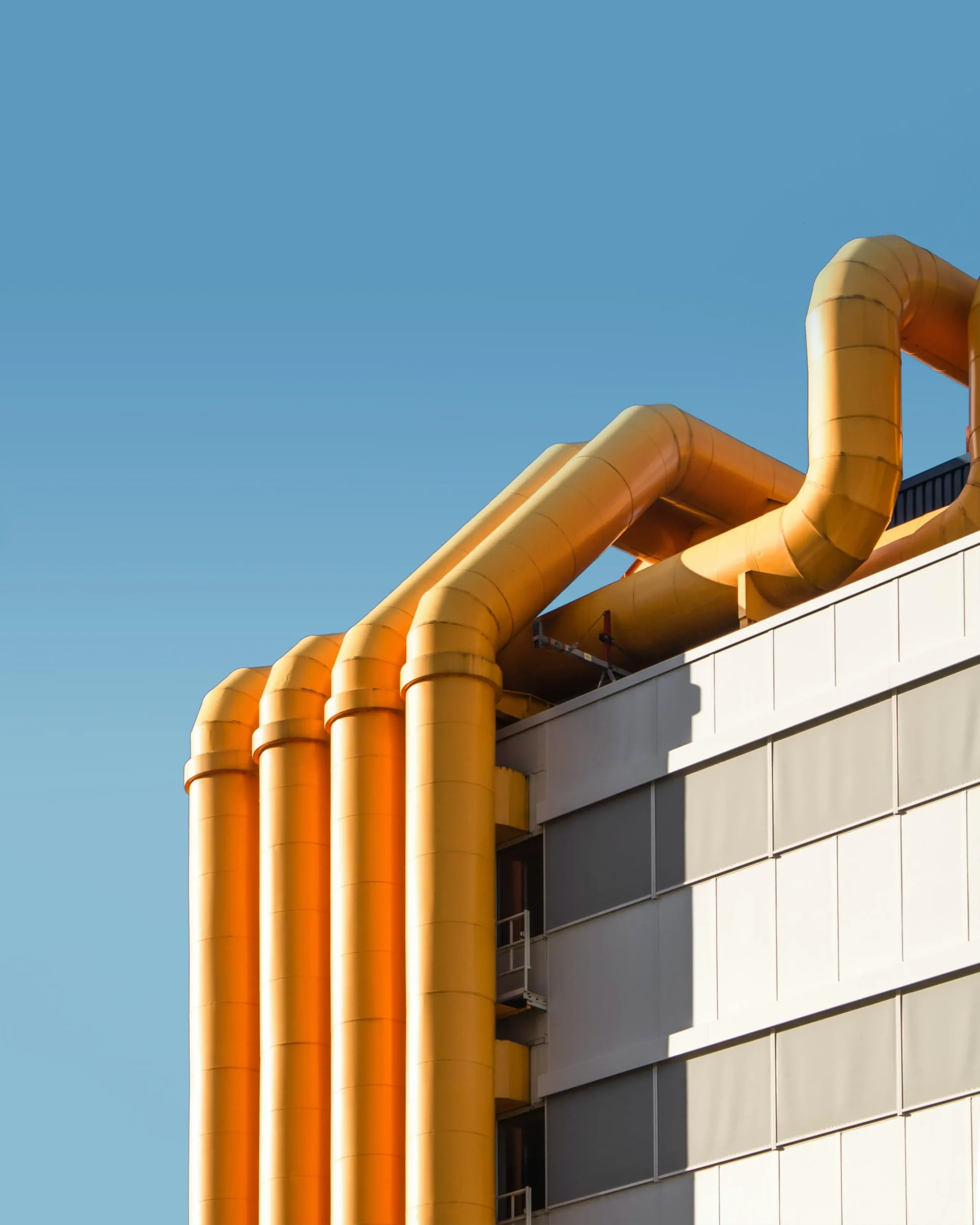

The advantages of waste heat
Now that we have a better understanding of what constitutes waste heat, the question arises: what makes this seemingly ‘leftover’ heat so valuable in the context of renewable energy? The answer lies in the multitude of benefits it brings:
- Sustainability: One of the most prominent benefits of waste heat is its contribution to sustainability. Reusing this leftover heat minimises waste and reduces reliance on conventional energy sources, thus minimising the ecological impact.
- CO2 reduction: Utilising waste heat helps reduce CO2 emissions. By optimising this energy source, we not only reduce our carbon footprint but also actively contribute to climate change mitigation.
- Cost savings: Waste heat offers economic benefits through the possibility of cost savings. Industrial processes can be made more efficient, resulting in lower energy costs and improved profitability for companies.
- Efficiency improvement: Reusing waste heat contributes to an overall improvement in energy efficiency. By reusing this heat for heating or electricity generation, we create a more circular approach to energy use.
This list of benefits makes it clear that waste heat is not only an untapped potential, but also a valuable asset in our efforts to achieve a more sustainable and efficient energy economy.
A more sustainable future
In the quest for a more sustainable future, utilising waste heat represents a promising and feasible step. With the capacity to reduce ecological impact, limit CO2 emissions and generate economic benefits at the same time, waste heat plays a crucial role in shaping a responsible energy economy.
By embracing this seemingly ‘surplus’ source of heat, we open the door to a more circular and efficient approach to energy use. Let us work together towards a more sustainable future, where waste heat no longer remains unused, but becomes an integral part of our efforts to transform the world into a resilient, green society.
Working on your ESG-innovation together with Beeliners
Do you have a good idea for a product, service, process or technological innovation that makes it easier to achieve ESG goals? And would you like to develop your idea in collaboration with Beeliners? Beeliners has an innovation cell dedicated to innovations in energy and heating systems. Feel free to drop by for a cup of coffee and we will be happy to discuss the possibilities with you.
Also interesting
-
How will the production of green gas be encouraged?
In an era when the world is paying increasing attention to renewable energy sources, green gas is a promising alternative that has the potential to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. Green gas, also known as biomethane, is produced from organic material such as green waste, sewage sludge, or even… Read More
-

What is bio-energy?
In an era when the urgency of renewable energy sources is becoming increasingly prominent, bioenergy takes centre stage as a promising and environmentally friendly solution. This renewable form of energy, derived from biological sources such as plants, offers a range of possibilities for reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and… Read More
-

This will encourage the use of renewable energy
In a world where the calls for sustainability and environmental awareness are getting louder, the use of renewable energy sources is central to the fight against climate change. While individual efforts by citizens and businesses play an important role, a crucial responsibility rests on governments worldwide to accelerate the transition… Read More

